Rund um den Eisprung
Der Eisprung ist das zentrale Element im weiblichen Zyklus – das Zusammenspiel verschiedenster Hormone sorgt dafür, dass die reife Eizelle den Eierstock verlässt und sich auf den Weg durch den Eileiter macht. Das ist der Zeitpunkt des Eisprungs – und erst ab dem Moment, in dem das Ei sich auf die Reise gemacht hat, ist eine Befruchtung möglich.
Es lohnt sich, den Eisprung selbst nochmal genauer unter die Lupe zu nehmen, denn er spielt eine große Rolle in der Familienplanung. Wenn Du weißt, wann genau Dein Eisprung stattfindet, kannst Du berechnen, wann Du fruchtbar bist und wann nicht.
Informiere Dich jetzt zu Deinem Eisprung und lerne Dich und Deinen Körper besser kennen.
Was ist der Eisprung?
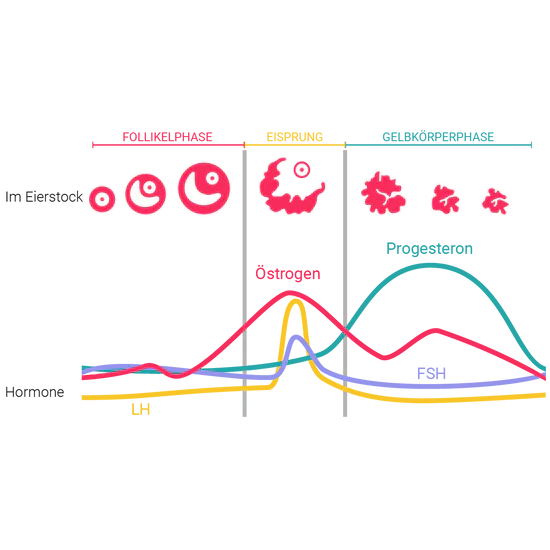
Der Eisprung ist der Moment, in dem die reife Eizelle aus den Eierstöcken in den Eileiter „springt“. Die reife Eizelle macht sich auf den Weg in die Gebärmutter (Uterus) und kann nun befruchtet werden.
Ausgelöst durch das Hormon FSH, wachsen mehrere Eizellen in den Eierstöcken heran. Rund um jede Eizelle befindet sich ein sogenanntes Eibläschen. In der Wand dieses Eibläschens wird das Hormon Östrogen gebildet.
Zwischen den heranreifenden Eibläschen kommt es zum Wettkampf: eines der Eibläschen wächst am schnellsten und meldet: ich bin soweit. Nun kommt das Hormon LH (Luteinisierende Hormon) zum Zug und es kommt zum sogenannten Eisprung: das Gewinner-Eibläschen platzt und entlässt die Eizelle in den Eileiter – wo sie sich auf den Weg Richtung Gebärmutter macht.
Wann findet der Eisprung statt?
In der Theorie (also bei einem ganz regelmäßigen Zyklus von 28 Tagen) findet der Eisprung statistisch am 14. Tag des Zyklus statt. In der Realität trifft diese Rechnung aber bei weit unter 20% der Frauen zu.
Wann verschiebt sich der Eisprung?
Der Zeitpunkt des Eisprungs kann sich in jedem Zyklus verändern. Die Hormone reagieren auf unsere Lebensumstände: die Eizelle wächst ja heran, um potenziell befruchtet zu werden und da schaut der Körper schon genau, wie die Umstände sind: Durch Stress, Krankenheiten, psychische Vorgänge, Reisen usw. kann sich der Eisprung verschieben und die Zykluslängen verändern.
Eine besondere Situation ist der erste Eisprung nach einer Entbindung. Wir haben dazu einen eigenen Beitrag verfasst, den findest Du hier: Eisprung nach der Geburt & in der Stillzeit.
Wie kann man den Eisprung berechnen?
Den Eisprung kann man nicht mathematisch oder statistisch anhand der Zykluslänge berechnen, denn diese Art der Berechnung nimmt keine Rücksicht auf die individuellen Gegebenheiten und Lebensumstände. Der Tag des Eisprungs kann in jedem Zyklus variieren – deshalb ist es wichtig, taggenau den aktuellen Fruchtbarkeitsstatus zu überprüfen und sich nicht nur auf den Kalender zu verlassen. Ob es auf den Eisprung zugeht oder ob er schon stattgefunden hat, kann man zum Beispiel durch die Beobachtung von Körperzeichen herausbekommen, also dem Verlauf der Körperkerntemperatur und des Zervixscheims – so, wie die symptothermale Methode es vorschreibt und trackle es umsetzt.

Das trackle Webinar
Du willst mehr über den Eisprung, Deinen Zyklus und trackle erfahren? Dann besuche jetzt unser kostenloses Online-Webinar!
Es erwarten Dich jede Menge spannende Informationen!
- Wie funktioniert der weibliche Zyklus?
- Wie bestimmt man den Zeitpunkt des Eisprungs?
- Was muss ich wissen, um hormonfrei zu verhüten?
Die fruchtbaren Tage
Wann bin ich fruchtbar?
Die Eizelle hält viel weniger lange durch, als viele meinen: nur circa 12 bis 18 Stunden, nachdem sie aus dem Eibläschen geplatzt ist, kann sie von einem Spermium befruchtet werden. Die Natur hat sich etwas Schlaues ausgedacht, um den Zeitraum zu verlängern: Spermien können im weiblichen Körper bis zu fünf Tage überleben – theoretisch reicht es also, vier Tage vor dem Tag des Eisprungs Vaginalverkehr zu haben, um das Befruchtungszeitfenster der Eizelle zu erwischen.
Wann genau sind die fruchtbaren Tage?
Die fruchtbaren Tage sind die Tage, an denen Du schwanger werden kannst. Da die Spermien bis zu fünf Tage im weiblichen Körper überleben können, bezeichnet man folgenden Zeitraum als fruchtbar: die vier Tage vor dem Eisprung, den Tag des Eisprungs selbst und die zwei Tage danach.
trackle weiß das alles: In der Auswertung in Deiner trackle-App werden alle fruchtbaren Tage um den Eisprung herum als solche angezeigt. Damit erkennst Du ganz exakt, wann Du fruchtbar bist.
Eisprung erkennen: Das sind die Anzeichen
Zervixschleim
Die Hormone Östrogen und Progesteron bewirken, dass der Zervixschleim sich verändert. Je näher der Eisprung rückt, desto glasiger und ziehbarer wird der Zervixschleim. Wenn Du ihn zwischen Deinen Fingern hast, zieht er Fäden – er ist spinnbarer. Vom Aussehen her erinnert er an rohes Eiweiß.
Muttermund
Der Muttermund oder Gebärmutterhals wird auch durch die Hormone des weiblichen Zyklus beeinflusst. Zu Beginn Deines Zyklus ist der Muttermund eher hart und ragt in die Scheide hinein. Rückt der Eisprung näher, wird der Muttermund weich, öffnet sich und steigt sogar etwas höher. Du kannst den Muttermund selber untersuchen, indem Du zwei Finger in die Scheide einführst und fühlst, wie sich der Muttermund anfühlt.
Temperatur
Das Hormon, das nach dem Eisprung ausgeschüttet wird – das Progesteron – bewirkt, dass Deine Körperkerntemperatur ansteigt – und das um circa 0,2°C. Es reicht allerdings nicht, die Temperatur nur einmal zu messen, denn die alleinige Höhe der Temperatur sagt Dir nicht, wie hoch das Progesteron ist. Um einen Anstieg festzustellen, brauchst Du deshalb einen Temperaturverlauf.
Mittelschmerz
Der Mittelschmerz ist ein Stechen oder Ziehen in der unteren Bauchhälfte und wird von einigen Frauen rund um den Eisprung beobachtet. Der Mittelschmerz ist kein Zeichen, dass der Eisprung gerade in diesem Moment stattfindet. Der Mittelschmerz tritt nur bei manchen Frauen in der Nähe des Eisprungs auf.
Zwischenblutung
Den Eisprung erkennst Du manchmal auch an Zwischenblutungen. Diese oder Schmierblutungen treten bei manchen Frauen in der Nähe des Eisprungs auf. Die Zwischenblutung ist entweder eine leicht rötliche Verfärbung des Zervixschleims oder sogar teilweise wie eine echte Blutung. Die Schmierblutung ist deswegen ein Zeichen von hoher Fruchtbarkeit.
Libido Veränderung
Viele Frauen berichten davon, rund um den Eisprung mehr Lust auf Sex zu haben. Grund für diese Libido-Veränderung ist wahrscheinlich die steigende Östrogenkonzentration. Da kommt wohl der Ur-Instinkt in uns hoch: Macht ja auch Sinn, während der fruchtbaren Zeit mehr Lust auf Sex zu haben – zumindest, wenn man es aus evolutionsbedingter und fortpflanzungsnützlicher Sicht sieht.
Wie trackle Dir dabei hilft, Deine fruchtbare Phase zu erkennen

Das trackle Webinar
Du willst mehr über den Eisprung, Deinen Zyklus und trackle erfahren? Dann besuche jetzt unser kostenloses Online-Webinar!
Es erwarten Dich jede Menge spannende Informationen!
- Wie funktioniert der weibliche Zyklus?
- Wie bestimmt man den Zeitpunkt des Eisprungs?
- Was muss ich wissen, um hormonfrei zu verhüten?




